Summarization-with-LangChain:Stuff — Map_reduce — Refine

I recently wrapped a tutorial on summarization techniques in LangChain. This article covers the basic usage of document summarization techniques and provides insights into various summarization methods. Additionally, to learn more and to explore how to validate intermediate results from the output of each of these techniques.
Link to the complete hands-on tutorial on Summarizer techniques
Reading_time: 7 min
Tags: [Langchain, LLM, GenAI, Summarizer]
- Summarization Techniques
- Stuff Chain
- Map-Reduce Method
- Refine Method
- Choosing the Right Technique
- Thanks for Reading!
Table of Contents:
I recently wrapped a tutorial on summarization techniques in LangChain. This article covers the basic usage of document summarization techniques and provides insights into various summarization methods. Additionally, to learn more and to explore how to validate intermediate results from the output of each of these techniques. For those interested in delving deeper into this topic, I invite you to explore the complete and comprehensive tutorial available here.
Summarization is a critical aspect of natural language processing (NLP), enabling the condensation of large volumes of text into concise summaries. LangChain, a powerful tool in the NLP domain, offers three distinct summarization techniques: stuff, map_reduce, and refine. Each method has its unique advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different scenarios. This article delves into the details of these techniques, their pros and cons, and the ideal scenarios for their application.
Complete implementation code and data used in the tutorial available in the below repository.
Summarization Techniques
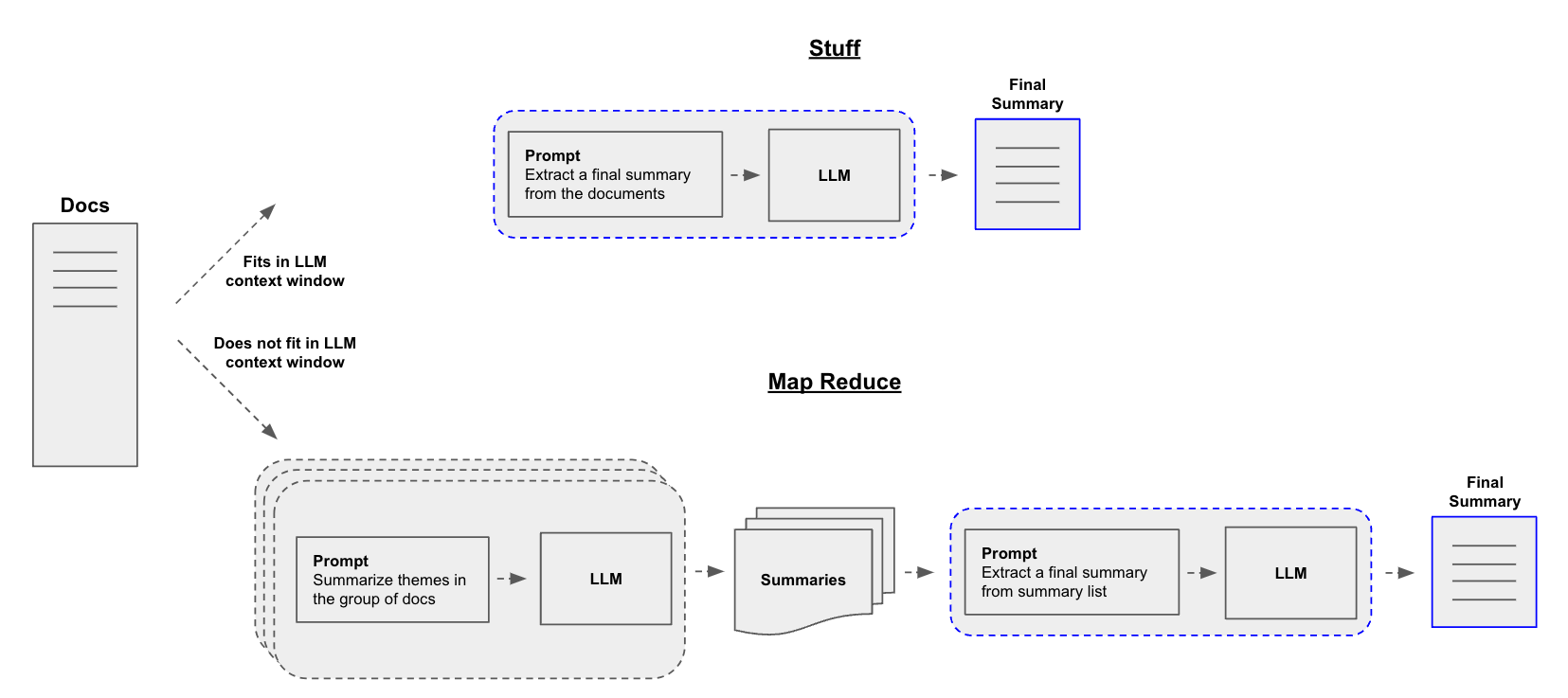
Stuff Chain
The stuff chain is particularly effective for handling large documents. It works by converting the document into smaller chunks, processing each chunk individually, and then combining the summaries to generate a final summary. This method is ideal for managing huge files and can be facilitated with the help of a recursive character text splitter.
Pros:
Efficiently handles large documents.
Allows for chunk-wise summarization, making it suitable for managing huge files.
Cons:
- LLM context window
Here’s an example of how to implement the stuff chain method:
from langchain.chains.combine_documents.stuff import StuffDocumentsChain
from langchain.chains.llm import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
#Define prompt
prompt_template = """Write a concise summary of the following:
"{text}"
CONCISE SUMMARY:"""
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(prompt_template)
#Define LLM chain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo-16k")
llm_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
#Define StuffDocumentsChain
stuff_chain = StuffDocumentsChain(llm_chain=llm_chain, document_variable_name="text")
docs = loader.load()
print(stuff_chain.run(docs))
Map-Reduce Method
The Map-Reduce method involves summarizing each document individually (map step) and then combining these summaries into a final summary (reduce step). This approach is more scalable and can handle larger volumes of text.The map_reduce technique is designed for summarizing large documents that exceed the token limit of the language model. It involves dividing the document into chunks, generating summaries for each chunk, and then combining these summaries to create a final summary. This method is efficient for handling large files and significantly reduces processing time.
Pros:
Effectively handles large documents by dividing them into manageable chunks.
Reduces processing time by processing chunks individually.
Cons:
- Requires extra steps in combining individual summaries, which can add complexity to the process.
Here’s an example of how to implement the Map-Reduce method:
from langchain.chains import MapReduceDocumentsChain, ReduceDocumentsChain
from langchain_text_splitters import CharacterTextSplitter
# Map
map_template = """The following is a set of documents
{docs}
Based on this list of docs, please identify the main themes
Helpful Answer:"""
map_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(map_template)
map_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=map_prompt)
# Reduce
reduce_template = """The following is set of summaries:
{docs}
Take these and distill it into a final, consolidated summary of the main themes.
Helpful Answer:"""
reduce_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(reduce_template)
reduce_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=reduce_prompt)
# Combine documents by mapping a chain over them, then combining results
map_reduce_chain = MapReduceDocumentsChain(
llm_chain=map_chain,
reduce_documents_chain=reduce_documents_chain,
document_variable_name="docs",
return_intermediate_steps=False,
)
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=0)
split_docs = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
print(map_reduce_chain.run(split_docs))
Refine Method
The Refine method iteratively updates its answer by looping over the input documents. For each document, it passes all non-document inputs, the current document, and the latest intermediate answer to an LLM chain to get a new answer. This method is useful for refining a summary based on new context.The refine technique is a simpler alternative to the map_reduce technique. It involves generating a summary for the first chunk, combining it with the second chunk, generating another summary, and continuing this process until a final summary is achieved. This method is suitable for large documents but requires less complexity compared to map_reduce.
Pros:
Simpler than the map_reduce technique.
Achieves similar results for large documents with less complexity.
Cons:
- Limited functionality compared to other techniques.
Here’s how you can implement the Refine method:
from langchain.chains.summarize import load_summarize_chain
prompt = """
Please provide a summary of the following text.
TEXT: {text}
SUMMARY:
"""
question_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=question_prompt_template, input_variables=["text"]
)
refine_prompt_template = """
Write a concise summary of the following text delimited by triple backquotes.
Return your response in bullet points which covers the key points of the text.
```{text}```
BULLET POINT SUMMARY:
"""
refine_template = PromptTemplate(
template=refine_prompt_template, input_variables=["text"]
# Load refine chain
chain = load_summarize_chain(
llm=llm,
chain_type="refine",
question_prompt=question_prompt,
refine_prompt=refine_prompt,
return_intermediate_steps=True,
input_key="input_documents",
output_key="output_text",
)
result = chain({"input_documents": split_docs}, return_only_outputs=True)
Choosing the Right Technique
The choice of summarization technique depends on the specific requirements of the task at hand. For large documents, the map_reduce and refine techniques are recommended due to their ability to handle chunk-wise summarization efficiently. The stuff chain is particularly useful for documents that are too large to be processed in a single go, offering a practical solution for managing huge files.
Each method has its advantages and is suitable for different scenarios. The Stuff method is straightforward but may not scale well with large volumes of text. The Map-Reduce method is more scalable and can handle larger documents but requires more setup. The Refine method is useful for iteratively refining a summary based on new context, making it a good choice for dynamic summarization tasks.
Thanks for Reading!
Connect with me on Linkedin
Find me on Github
Visit my technical channel on Youtube
Support: Buy me a Cofee/Chai